What is Plastic Injection Molding and How Does It Work?
Plastic injection molding has revolutionized the manufacturing industry. This process allows companies to produce complex parts at scale. According to John Smith, a leading expert in plastic injection molding, "This technology transforms ideas into reality."
At its core, plastic injection molding involves injecting molten plastic into a mold. The process requires precision, skill, and attention to detail. Many manufacturers rely on this technique for its efficiency. However, challenges often arise. For instance, selecting the right materials is crucial. Poor choices can lead to product failures.
Understanding the intricacies of plastic injection molding is essential. It is not just about machinery and molds. It requires thorough planning and quality control. Each step impacts the final product. Embracing imperfections can lead to valuable improvements in strategy. The world of plastic injection molding is both challenging and rewarding.

What is Plastic Injection Molding?
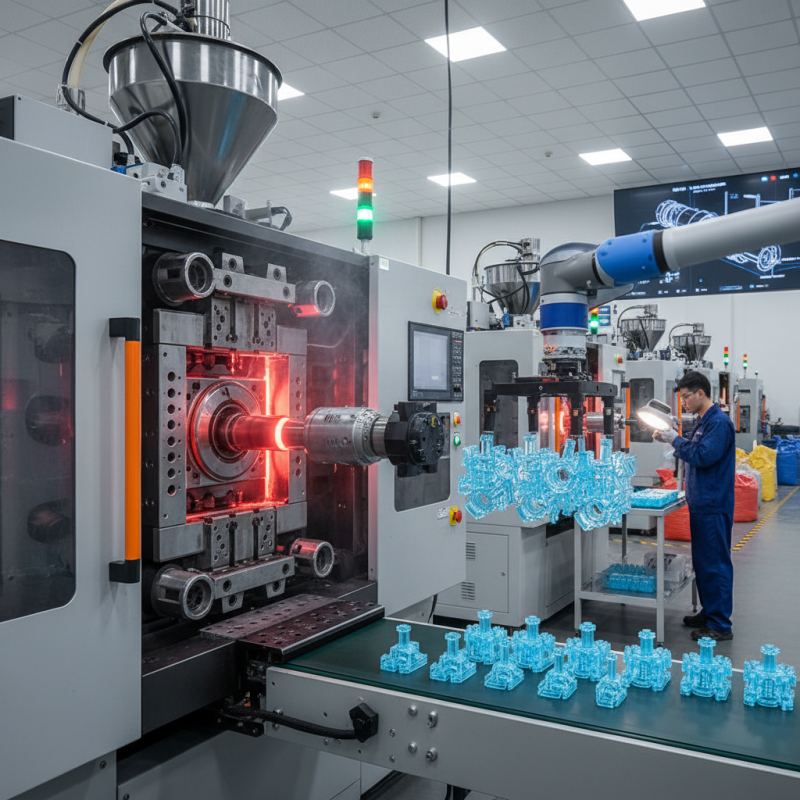
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process used to create items from plastic materials. It involves melting plastic and injecting it into a mold. Once cooled, the mold is removed, revealing a finished product. This technique is popular for its efficiency and ability to produce complex shapes.
The process begins with plastic pellets, which are heated until they become liquid. Then, the liquid is injected into a metal mold. Many molds are reusable, allowing for high-volume production with minimal waste. However, achieving perfect quality can be challenging. Minor inconsistencies in heating can lead to defects. Manufacturers often need to adjust temperatures and pressure.
For industries, precision is key. Even small errors can lead to faulty products. Regular maintenance of equipment is crucial for consistent outcomes. While injection molding offers many advantages, flaws can happen. Learning from these imperfections is essential for improvement. Each new production run provides lessons for better results.
Key Components of Injection Molding Machines
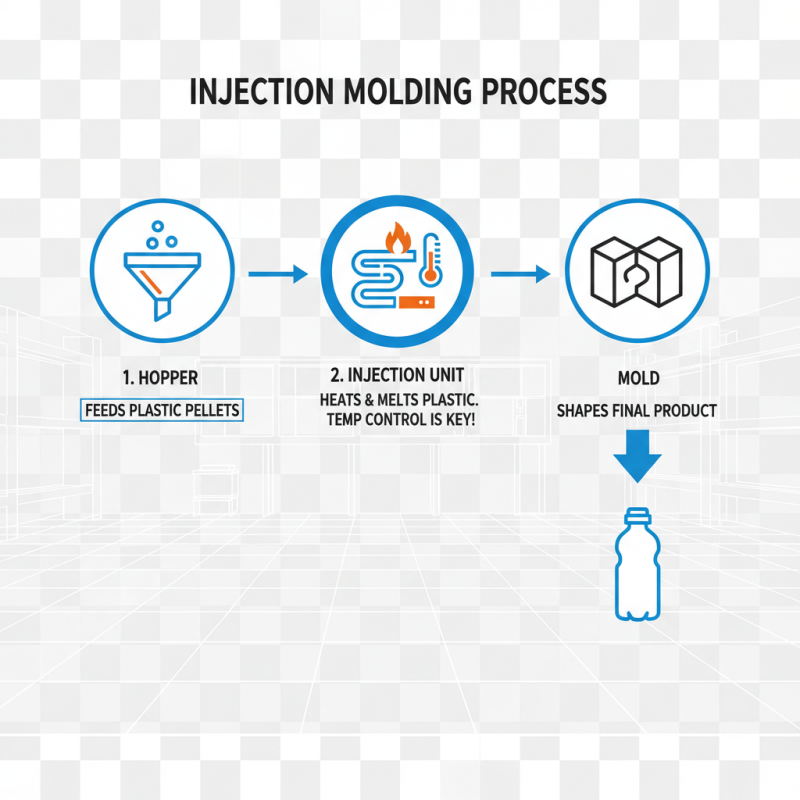
Injection molding machines consist of crucial components that work together to produce plastic products efficiently. The primary parts include the hopper, injection unit, and mold. The hopper feeds raw plastic pellets into the machine. These pellets are heated in the injection unit until they become molten. Proper temperature control is vital here; otherwise, the material may degrade.
The mold is where the magic happens. It shapes the molten plastic into the desired form. Creating molds can be costly and time-consuming. However, their precision impacts the final product quality significantly. A slight misalignment might ruin the entire batch. Regular maintenance of both the mold and the machine is essential to ensure consistency.
Tips: Always monitor the machine settings. Even minor changes in temperature can affect the outcome. Begin with small batches to identify any issues. Don't hesitate to adjust the mold design based on feedback. This approach ensures you continually improve the production process.
The Injection Molding Process: Step by Step
The injection molding process involves several key steps. Initially, raw plastic pellets are heated in a barrel until they melt. This molten plastic is then injected into a mold under high pressure. The mold is typically cooled, allowing the plastic to solidify into the desired shape. Once cooled, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected. This process is efficient and allows for high-volume production.
Tips: Pay close attention to mold temperature. Too hot can cause defects; too cold can lead to incomplete fills. Adjust these parameters for better results.
After the part is ejected, it may require finishing touches. Sometimes, additional steps like trimming or polishing are necessary. Inspecting the molded parts is crucial. Minor imperfections can affect functionality. Always review the process to ensure quality standards are met.
Tips: Consider the cycle time for each injection. Reducing cycle time can increase overall production efficiency. However, rushed processes can lead to errors. Striking a balance is vital.
What is Plastic Injection Molding and How Does It Work?
| Step | Description | Materials Used | Cycle Time (Seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Material is fed into the hopper. | Thermoplastics, Thermosetting plastics | 2-5 |
| 2 | Material is heated and melted in the barrel. | Polyethylene, Polypropylene | 5-10 |
| 3 | Molten plastic is injected into the mold. | PVC, Nylon | 1-3 |
| 4 | Cooling occurs, solidifying the plastic. | Polystyrene, ABS | 10-30 |
| 5 | Mold is opened, and the part is ejected. | Various plastic types as per specs | 3-7 |
Applications of Plastic Injection Molding in Various Industries
Plastic injection molding is a versatile manufacturing process used across various industries. This method allows for the mass production of plastic parts with high precision. It is widely adopted in automotive, consumer goods, and medical applications. In the automotive sector, for example, components such as dashboards, bumpers, and interior parts are crafted using this technique. It ensures durability and lightweight characteristics, ultimately enhancing vehicle performance.
In the consumer goods arena, plastic injection molding creates everything from kitchen utensils to electronic casings. The technique enables manufacturers to produce complex designs quickly and efficiently. However, challenges can arise in the form of mold design and material selection. Each product must be assessed to prevent defects that could lead to faults in the final item. In medical applications, precision is paramount. Here, molded parts must meet strict regulatory standards, balancing quality with practicality. Despite the advantages, achieving the perfect mold can sometimes require multiple iterations and thorough testing. Thus, manufacturers are often in a continuous loop of improvement.
Applications of Plastic Injection Molding in Various Industries
Advantages and Challenges of Plastic Injection Molding
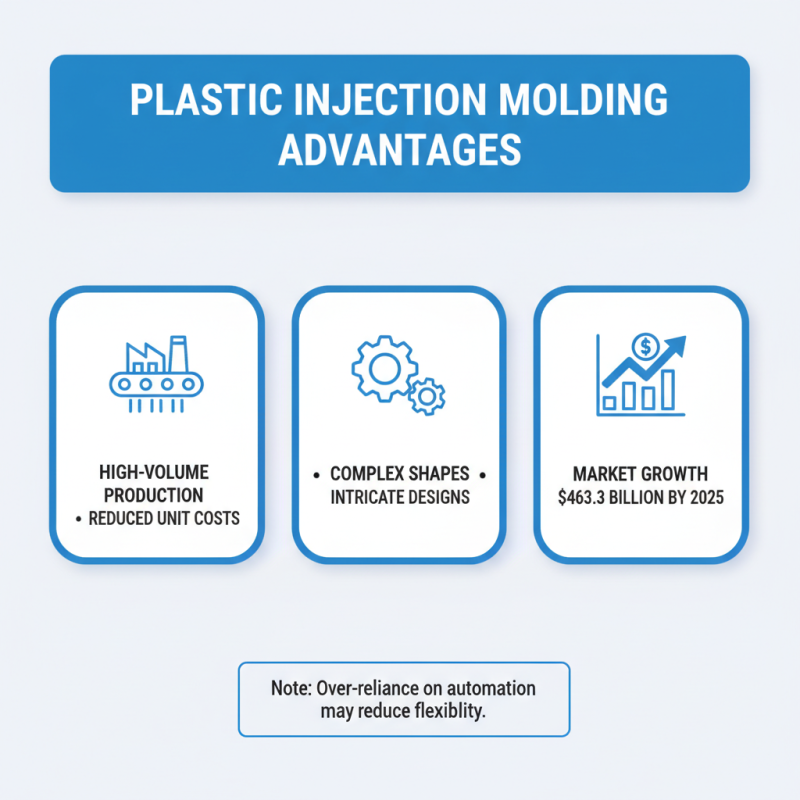
Plastic injection molding offers several advantages that make it a popular choice in manufacturing. It enables high-volume production, which can significantly drive down unit costs. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global plastic injection molding market is projected to reach $463.3 billion by 2025. This indicates a strong demand for efficient production methods. The ability to create complex shapes and intricate designs is another key benefit. However, becoming too reliant on automated processes can reduce flexibility.
The challenges in plastic injection molding are equally important to consider. A common issue is material waste. Although modern technologies can minimize waste, manufacturing still generates excess material. In some cases, this can be as high as 20%. Additionally, ensuring product quality can be difficult. Flaws like sink marks or warping can occur if the process is not carefully controlled. These problems can lead to costly rework or even loss of reputation.
Sustainability concerns also add another layer of complexity. While plastics are versatile, their environmental impact is a growing issue. Many manufacturers are looking for ways to incorporate recycled materials. However, this can affect product performance. Balancing efficiency and sustainability can be tricky, and industry players must continue exploring innovative solutions to address these challenges.
Related Posts
-

Innovative Examples of Automotive Injection Molding Applications in the Industry
-

Essential Checklist for Quality Assurance in Plastic Injection Molded Parts Production
-

In Depth Comparison of Plastic Injection Mold Tooling Techniques and Their Industry Impact
-

Exploring the Future of Manufacturing: How Plastic Injection Molded Parts Transform Industries
-

Unlocking Efficiency: How Precision Plastic Injection Molded Parts Boost Production by 30% in Manufacturing
-

Maximizing Efficiency in Plastic Injection Mold Tooling for High Volume Production

